New Moon – the Invisible Phase
The New Moon is when the Sun and Moon are aligned, with the Sun and Earth on opposite sides of the Moon.
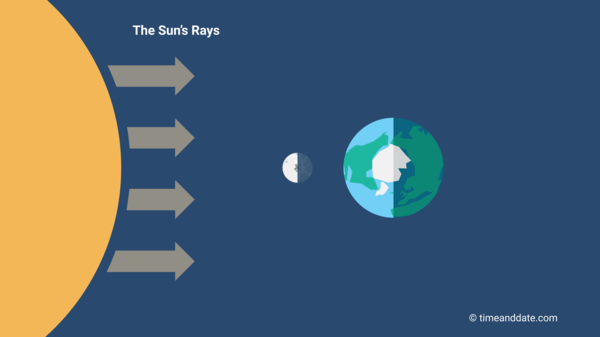
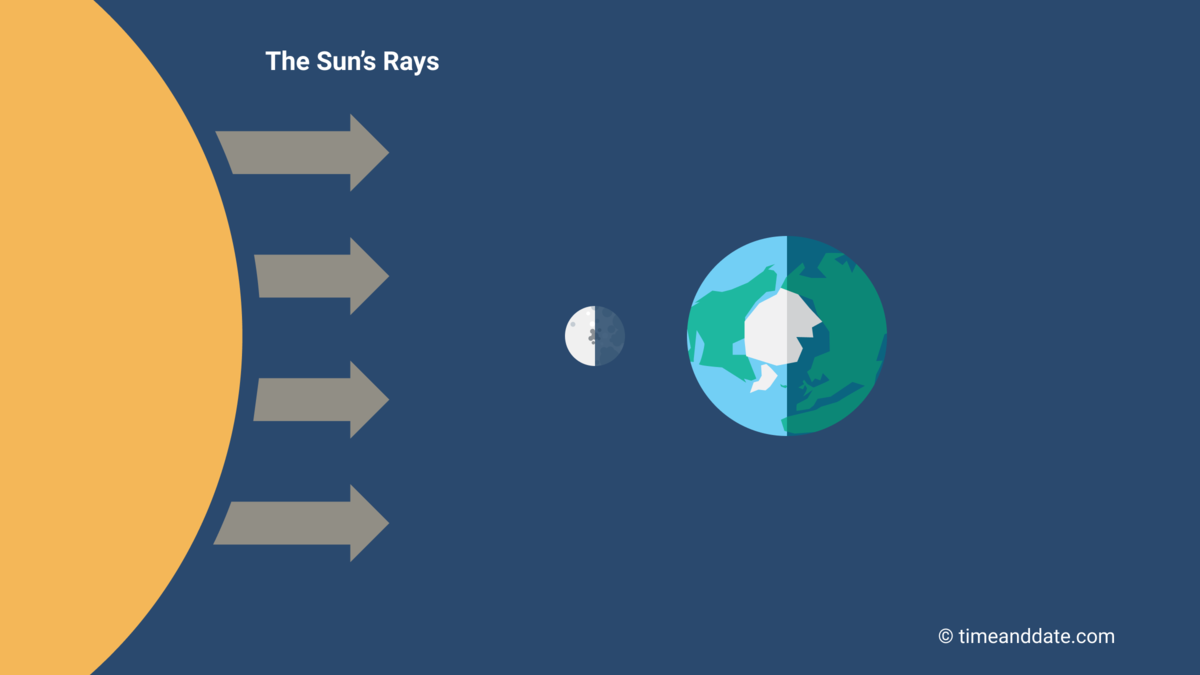
At New Moon, the Sun, the Moon, and Earth are in alignment.
©timeanddate.com
Why do some get a Black Moon in November?
Dec 7: Don’t miss the Moon and Saturn meeting in the sky
Look out for December’s extreme Full Moon
Next New Moon
31 Dec 2024, 06:26
Previous New Moon
1 Dec 2024, 14:21
Times for the New Moon vary by time zone. Times and dates are based on the local time in Hong Kong. Change location
We Can’t See the New Moon
There are two reasons why we can’t see the New Moon:
- The alignment of the Sun, the Moon, and Earth leaves the side of the Moon that faces Earth in darkness. This is called a conjunction or syzygy.
- The New Moon is up in the daytime sky. It rises and sets around the same time as the Sun, bringing it too close to the Sun’s glare to be seen with the naked eye.
For all that, however, there is one special occasion when we can see a New Moon: during a solar eclipse. In fact, this is the only occasion that the New Moon is “perfect”. The Moon’s orbit around the Earth is slightly tilted, which means that—more often than not—the Sun, Moon and Earth are not perfectly aligned at New Moon. With specialist equipment, it is sometimes possible to detect a vanishingly thin lunar crescent in the blue sky at the precise moment of New Moon.
The Moon: Our natural satellite
A Good Night for Stargazing
As New Moon nights are dark, they are often the best time to view other celestial objects like planets, meteor showers, the Milky Way, and deep sky objects such as star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies.
Half of the Moon’s surface is always illuminated by direct sunlight, except during lunar eclipses when Earth casts its shadow on the Moon. Just how much of that light we can see from Earth varies every day, and we call this a Moon phase.
Is there a dark side of the Moon?
Higher Tides at New Moon
The greatest difference between high and low tide is around New Moon and Full Moon. During these Moon phases, the Moon and the Sun’s gravitational forces combine to push the ocean’s water in the same direction. These tides are known as spring tides or king tides.
Sleep, crime, and menstruation: how Moon phases affect humans
Religious and Cultural Significance
About a day after the New Moon conjunction, the Moon becomes visible again. The initial period, as only the thinnest sliver of a Crescent Moon becomes visible, used to be called New Moon, while the darkest phase was called Dark Moon.
This traditional definition of the New Moon is still in use in some cultures, defining the beginning of the months in the Islamic calendar.
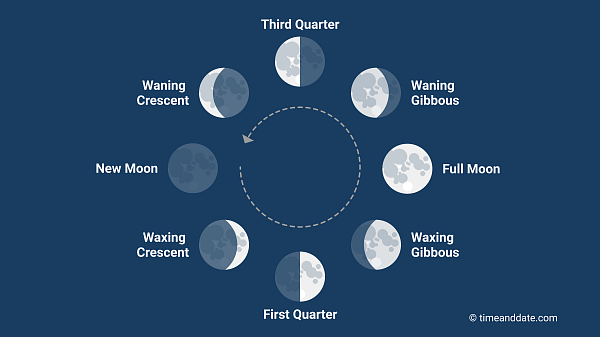
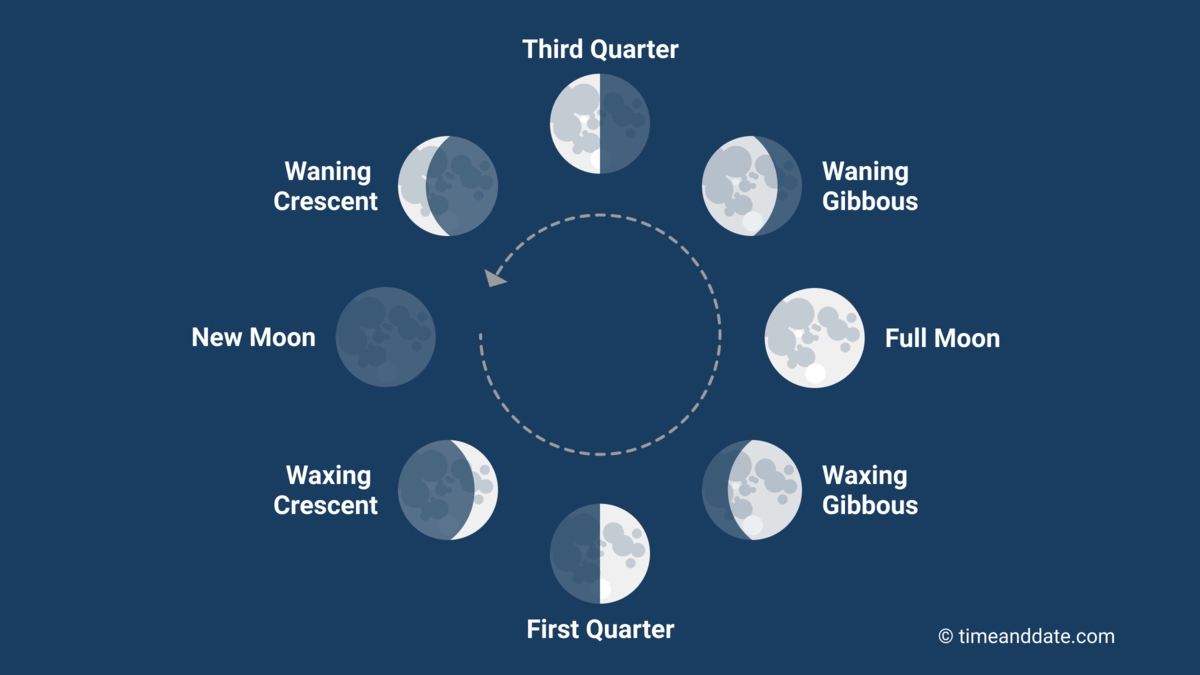
It takes around 29.5 days to move through the eight Moon phases.
©timeanddate.com
First Primary Moon Phase
In western culture, we divide the lunar month into four primary and four intermediate Moon phases.
The New Moon is the first primary Moon phase. The next three are the First Quarter Moon (Half Moon), the Full Moon, and the Third Quarter Moon (Half Moon).
In addition, there are four intermediate Moon phases; the Waxing Crescent Moon, the Waxing Gibbous Moon, the Waning Gibbous Moon, and the Waning Crescent Moon.
New Moon Symbol in Calendars

The symbol for New Moon in modern calendars is a filled, black circle.
The other primary Moon phase symbols in calendars: = First Quarter,
= Full Moon,
= Third Quarter
Causes Solar Eclipses
Two to three times a year, the New Moon phase coincides with the Moon reaching the lunar nodes of its orbit. The lunar nodes are the points where the Moon’s orbit crosses the ecliptic, which is the Sun’s path, seen from Earth. Then, the New Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun and becomes visible as a silhouette in front of the Sun.
Solar eclipses can only happen in the hours around New Moon. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, only occur at Full Moon.
When Is the Next Solar Eclipse?

A total solar eclipse is a New Moon eclipsing the Sun.
©bigstockphoto.com/JohanSwanepoel
A Black Moon Is a New Moon
Most years have 12 New Moons, one each month. But our calendar is not perfectly synchronized with astronomical events. Therefore, every now and then, a year has 13 New Moons. When this happens, at least one of those New Moons is a Black Moon.
Super and Micro New Moon
The Moon orbits Earth on an elliptical path, so its distance from Earth changes during a lunar month.
The point closest to Earth is called perigee, and the farthest point is known as apogee. When the New Moon is close to the perigee, it is known as a Super New Moon.
A Micro New Moon, on the other hand, is when it is farthest from Earth, at apogee.